The site was used as a radar installation and coastal defense site. Concrete bunkers were built to house the radar units and diesel generators that powered them. The campsite was used to house the personnel that operated the site.
The 6-acre campsite was returned to G.R. Daley on January 10, 1947. The old campsite is currently a private campsite called Thousand Trails Pio Pico and is owned by Thousand Trails. The 3560.09 acres were returned to the Department of the Interior on February 8, 1949 and are in use as a communication complex by the federal government under the authority of the Bureau of Land Management. The 4.85-acre right-of-way lease with the Otay Agricultural Corporation was terminated on January 4, 1949. Information regarding current use of the 4.85-acres is not available. No information was found under the name of the Otay Agricultural Corporation.

The site was used as a radar installation, known as Radar Station AWS B-8/J-8, and coastal-defense site. The campsite was known as Camp Minnewawa, and was used to house the personnel that operated the site. Concrete bunkers were built to house the radar units and the diesel generators that powered them. 3. The 6-acre campsite was returned to G·.-R. Daley on January 10, 1947. The old campsite is currently a private campsite called Thousand Trails, Pio Pico and is owned by Thousand Trails. The 3560.09 acres were returned to the Department of the Interior on February 8, 1949, and are Public Domain Lands. The 4.85-acre right-of-way lease with Otay Agricultural Corporation was terminated on January 4, 1949. The site currently contains communications equipment near the summit of Otay Mountain. Additionally, the site is heavily patrolled by the US Border Patrol.

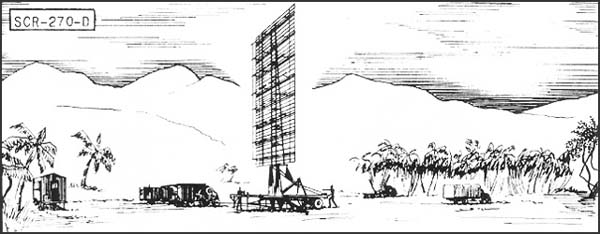
| Altitude, feet | 1,000 | 5,000 | 20,000 | 25,000 |
| Range, miles | 20 | 50 | 100 | 110 |
- Set should be sited at a height
between 100' and 1000' above an unobstructed reflecting surface.

| Altitude, feet |
|
|
|
|
| Range*, miles |
|
|
|
|
- *Range of PPI limits GCI operation
to about 45 miles.